Frontline physician Tim Jagatic on the worst Ebola outbreak in history
Dr. Jagatic on the disease’s stigma and whether or not it could spread beyond West Africa
Share
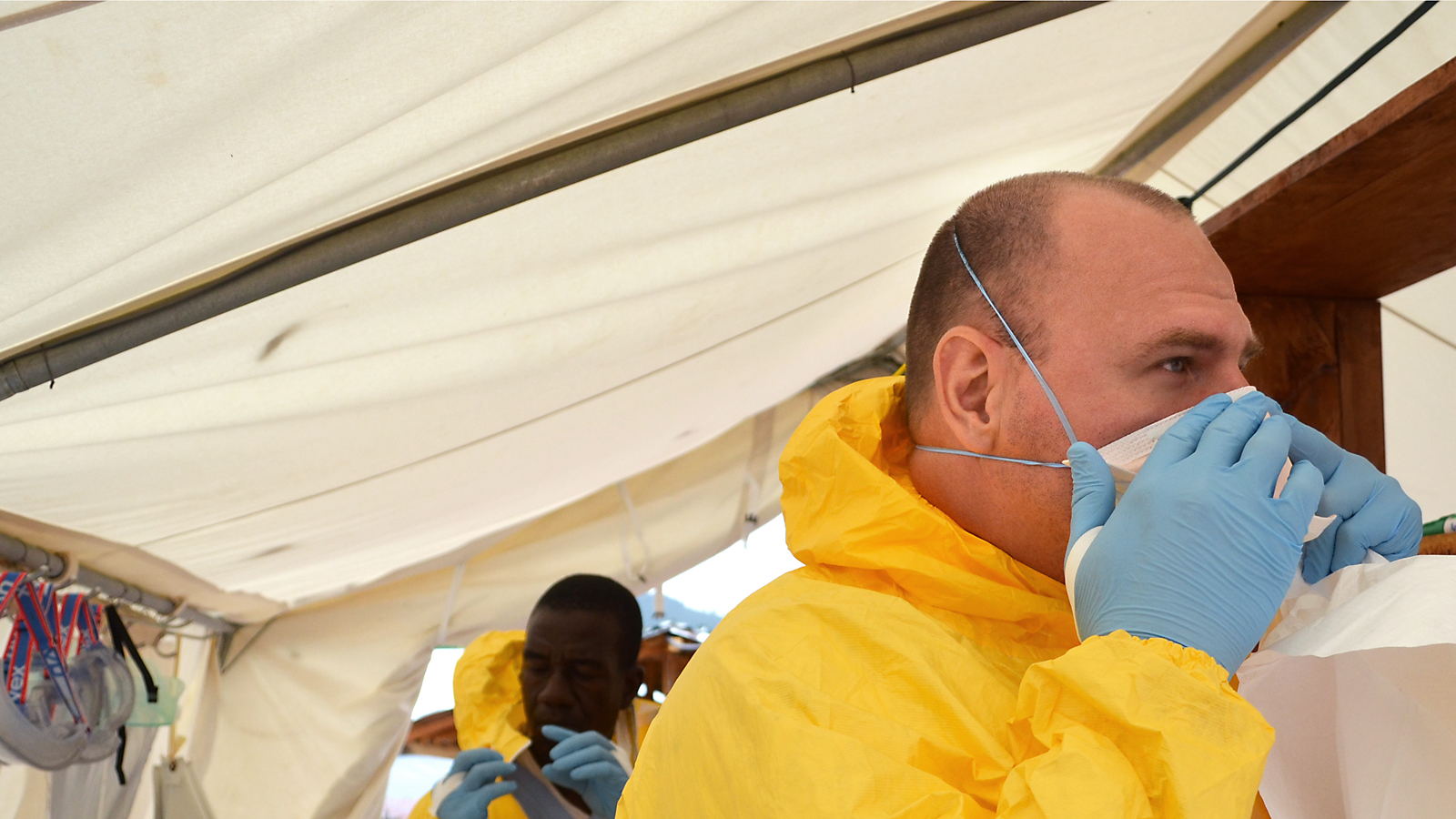
Few diseases inspire more terror than Ebola. The deadly virus causes rapidly worsening fever and pain, internal hemorrhages and, usually, death. Most patients spend their last days in isolation, sometimes bleeding from their eyes and nose, surrounded by people in Hazmat-style suits and goggles. Some suspect the current outbreak originated among bat hunters near Guéckédougou, Guinea. Since February, it has spread to 1,093 people and killed 660 in the West African countries of Liberia, Guinea and Sierra Leone. Family doctor and native of Windsor, Ont., Tim Jagatic is on the ground in Kailahun, Sierra Leone, helping Doctors Without Borders fight the worst Ebola outbreak in history.
Q: How does this illness present? What is actually happening?
A: When the virus enters the body, it attacks the immune system and the blood vessels. It releases an immune cascade at the same time as your blood vessels are being weakened. On the outside, you see fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, joint pain, muscle pain—a lot of things people associate with the common cold. With the progression of the disease, you might see the hemorrhagic signs. We see that in fewer than 50 per cent of cases.
Q: What are the hemorrhagic signs?
A: We see people with nosebleeds. They have bloody vomit, bloody diarrhea, internal bleeding and conjunctivitis [bloodshot eyes].
Q: What’s the usual cause of death?
A: There are many, and because it’s such a large outbreak, we’re starting to see some signs that we didn’t associate with Ebola before. We saw some patients with elevated blood sugar. We’ve seen people dying from what seemed to be a heart attack. We’ve seen people dying from blood loss. We’ve seen people just being overwhelmed by the disease. We don’t have much diagnostic material to work with, so we’re not able to do an EKG to see if it was a heart attack or not.
Q: You were in the outbreak zone back in March and April, in Guinea. What has changed?
A: I was there for about three weeks. I saw an epidemiologist, and he said, “We’re seeing the tip of the iceberg.” Plain and simple: The virus has gotten to a point where it’s able to spread itself, just because it’s a capital city, and within a population with a cultural practice that lets this virus spread around.
Q: How is it spreading within communities?
A: Funerals are the biggest point of infection. When one person dies, people from all over will come and practise their behaviour rituals [touching and kissing the unembalmed body without washing their hands after]. A dead body is the most infectious thing, and that’s when the majority of people come into contact with it. Another one is being exposed to sick people. The whole family is taking care of them, being exposed constantly.
Q: What would you be doing in an ideal situation to respond to Ebola?
A: We need twice as many people. We simply don’t have the numbers to delegate all the things that have to be done when we’re in the isolation ward. Because we’re wearing personal protective equipment, it limits the amount of time that we spend inside the isolation unit. We would like to keep a visit between 45 minutes and one hour, but now, we’re stretching it to almost two hours. We put ourselves through a very strong physiological stress when we’re using personal protection gear, because it’s impermeable. So we sweat, we’re losing water, we’re getting hotter and it wreaks havoc on the body. Our own endurance starts to wear down.
Q: What treatment can you provide?
A: The treatment is supportive therapy. Someone has a fever; we give them Tylenol. If someone has diarrhea, we give fluids. We provide high-quality nutrition. We also provide a round of antibiotics for any side bacterial infections. We do a whole bunch of things to push away any distraction the immune system might have from fighting the disease.
Q: It’s suspected the strain is Zaire ebolavirus. The mortality rate is as much as 90 per cent. What levels of mortality are you seeing?
A: I don’t have the numbers in Sierra Leone. Patients are coming in with much later disease progression. Back in Guinea, we were running at about 50 per cent survival. There’s a little town just about an hour and a half north of Conakry, and there was immediate organization of the community and [Doctors Without Borders] together. It was explained to them how the virus was spread, what to do to prevent the spread, what the symptoms look like and how it’s important to come to treatment. In this little village, we had a survival rate of 75 per cent. Because people were coming in early, the outbreak was shut down in one month. The 90 per cent mortality is associated with when nothing is done.
Q: There have been some erroneous local beliefs and some negative practices in response this outbreak. How are you responding?
A: Yeah, it’s really important for us to understand why it’s happening. In Guéckédougou [in Guinea], the people had a person die in their village. That happens. The next day, [health workers] show up in space suits and start spraying everything [with disinfectant]. And then more people started dying. So it seems [to them] like after we showed up with the spray, more people died. And they say, “Oh, so you’re spraying Ebola in our village.” This was the line of reasoning. It’s difficult to explain that there’s something so small, you can’t see it with your own eyes, but it’s one of the deadliest things. We take for granted our basic level of education in the West.
Q: Can you give me an idea of the panic? What about you? You could get it, too.
A: In the community, the biggest point of fear is the unknown. They know something bad called Ebola is in their community, and it’s killing people they know and love, and they don’t know how to stop it. On a personal level, when I’m dressed up in my full personal protection equipment, I know I am not exposed to the virus. When we’re back in our compound, we’ve gone through multiple decontaminations. There are all these checkpoints to make sure we’re washing our hands. Also, we know how the virus is spread, so we know how to avoid being contaminated. There is a very strong sense of safety.
Q: But it is killing health care workers: at least one Ugandan doctor, at least one nurse.
A: Potentially they weren’t aware of what they were dealing with, so they might have been more relaxed. They might not have worn gloves. They might have got body fluids with high viral loads on their skin, then made contact with their mucous membranes. The virus is not that contagious: I can have a conversation with someone who is infected, with no more than three feet between us and no mask, because we’re separated. The virus is not aerosolized. When we’re in closer vicinity, when we’re being exposed to bodily fluids, we take more precautions.
Q: Putting someone in isolation is not a normal cultural practice. Is it having an effect on well-being?
A: We do address this. Today, we had two or three family members of different patients come in. They got dressed up in personal protective equipment. We went in there with them, and we explained what to do. We also have other areas set up. Because the isolation unit is in tents and we just have fencing as our barriers, we have chairs family members can sit on outside. The patients sit inside, and they’re able to talk normally with each other. Also, social bonding is forming among many of the patients. I’d say there’s a good 10 to 15 patients in there who will survive. This group of women are sitting there during lunchtime, and because it’s kind of boring, sitting in these isolation units, they become friends, they’re gossiping, they’re having a good time, almost.
Q: It’s interesting that’s happening in the hospital, because there’s some stigma in communities. Have you seen that?
A: Oh, yes. There was a group of seven people dropped off at our hospital yesterday, because they were believed to have been in contact with somebody who had Ebola. They were shunned. Rocks were being thrown in their direction. When our ambulance showed up to deal with the dead body, the leader of that community forced our ambulance to take those people. Two of them ended up being feverish, so we kept them in our ward for suspected cases. But we had to have a long discussion with community leaders.
Q: Can you see Ebola spreading beyond West Africa?
A: I find that highly unlikely, simply because the world is on high alert about West Africa right now. We have such strong public health measures and such strong infrastructure in the West. It wouldn’t allow the virus to spread.
Q: What’s been the most challenging part for you, personally?
A: We saw one of our own staff members test positive, a local staff member [in Guinea]. He showed up with a fever. He was feeling nauseous and he had diarrhea and vomiting. We did blood tests, and then I went back to Brussels. I got a phone call to let me know that he did test positive. It was hitting close to home. He did get infected before he started working with us.
Q: You’re taking so many precautions, but the risk is there. Are your loved ones okay with you going into an Ebola zone?
A: They’re not the happiest, but they understand why I’m doing it.
Q: And why are you doing it?
A: There’s a need for it, plain and simple. I have the training to help bring an end to this problem, so I’ll give everything I can.